本章是整理知识内容,为强化知识长期更新。
Spring Web MVC
Spring Web 模型-视图-控制器 (MVC) 框架围绕
DispatcherServlet将请求分派给处理程序而设计。
常用注解
@Controller
- 声明在类上,该注解表明该类扮演控制器的角色,类似Action。
@RestController
- RestController是Controller超子集,相当于@RequestMapping方法默认采用@ResponseBody注解。
@RequestMapping
- 该注解是用来映射一个URL到一个类或一个特定的方处理法上。
- RequestMapping属性
- path / method 指定方法的映射路径
- params / headers 请求映射范围
- consumes / produces 请求与响应格式的限制范围
- Restfull风格的使用。
- restfull 支持的请求头GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE 。
- 通常情况下只使用 GET,PUT,POST,DELETE。
- GET 通常用来获取数据。
- PUT 通常用来新增数据。
- POST 通常用来更新数据。
- DELETE 通常用来删除数据。
@RequestMapping(value = "/get", method = RequestMethod.GET) public Object get(){ return "200"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/post", method = RequestMethod.POST) public Object post(){ return "200"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/delete", method = RequestMethod.DELETE) public Object delete(){ return "200"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/put", method = RequestMethod.PUT) public Object put(){ return "200"; }
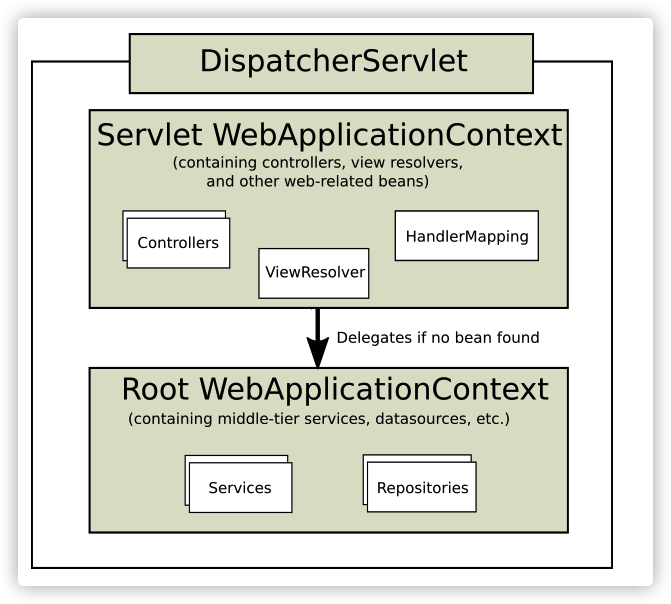
DispatcherServlet
- Root WebApplicationcontext 是可以在不同的 Servlet WebApplicationcontext共享,但是反来不醒,因此通常将web相关的代码放到Servlet WebApplicationcontext一些基础代码放到Root WebApplicationcontext 。也可以让Root WebApplicationcontext 托管所有的bean,这样可以避免Servlet WebApplicationcontext未初始化全部bean的问题。
源码分析
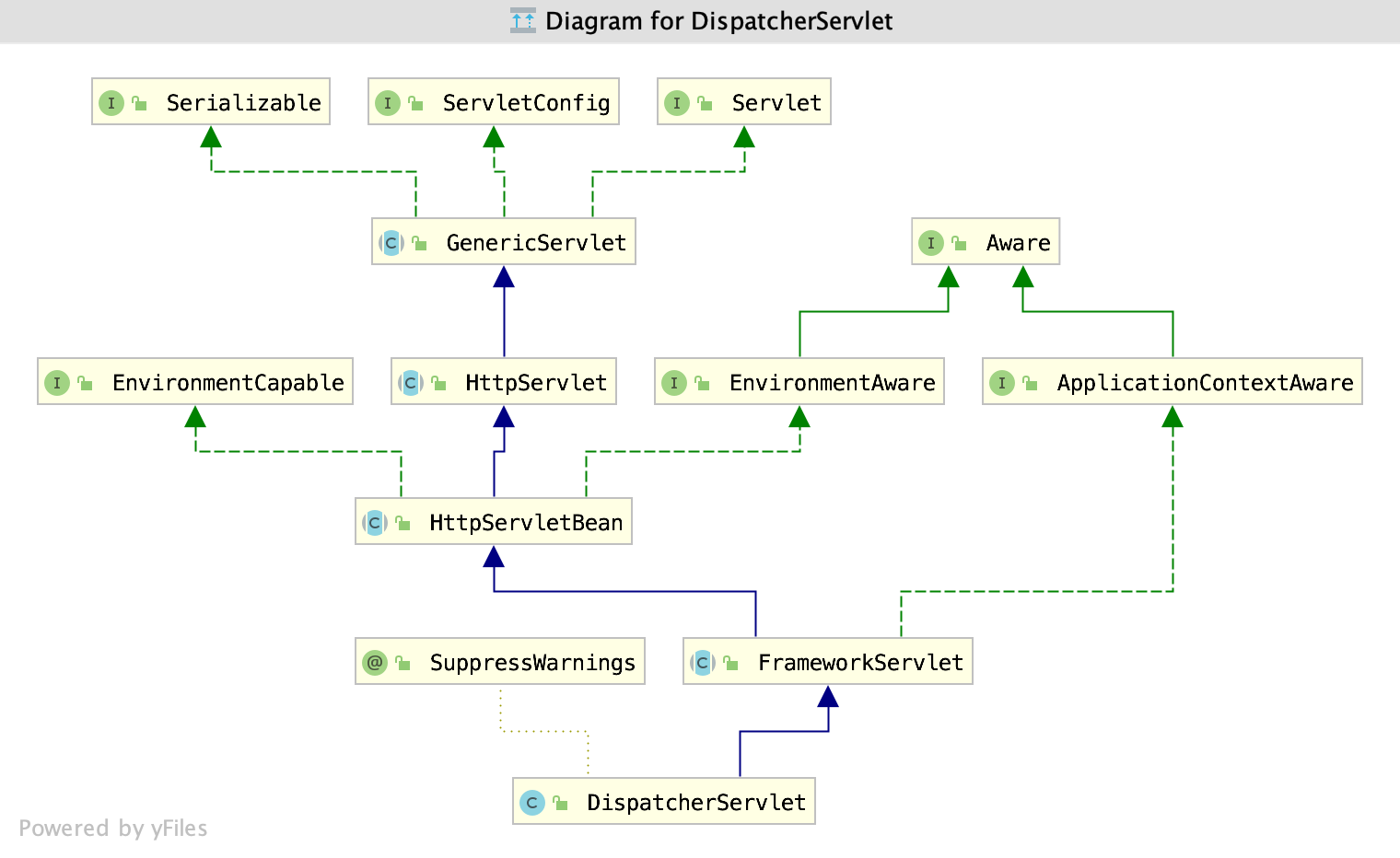
DispatcherServlet是继承了FrameworkServlet,而FrameworkServlet又继承了HttpServletBean。追溯到最上层其实就是Servlet。通过源码可以发现最核心的一个方法
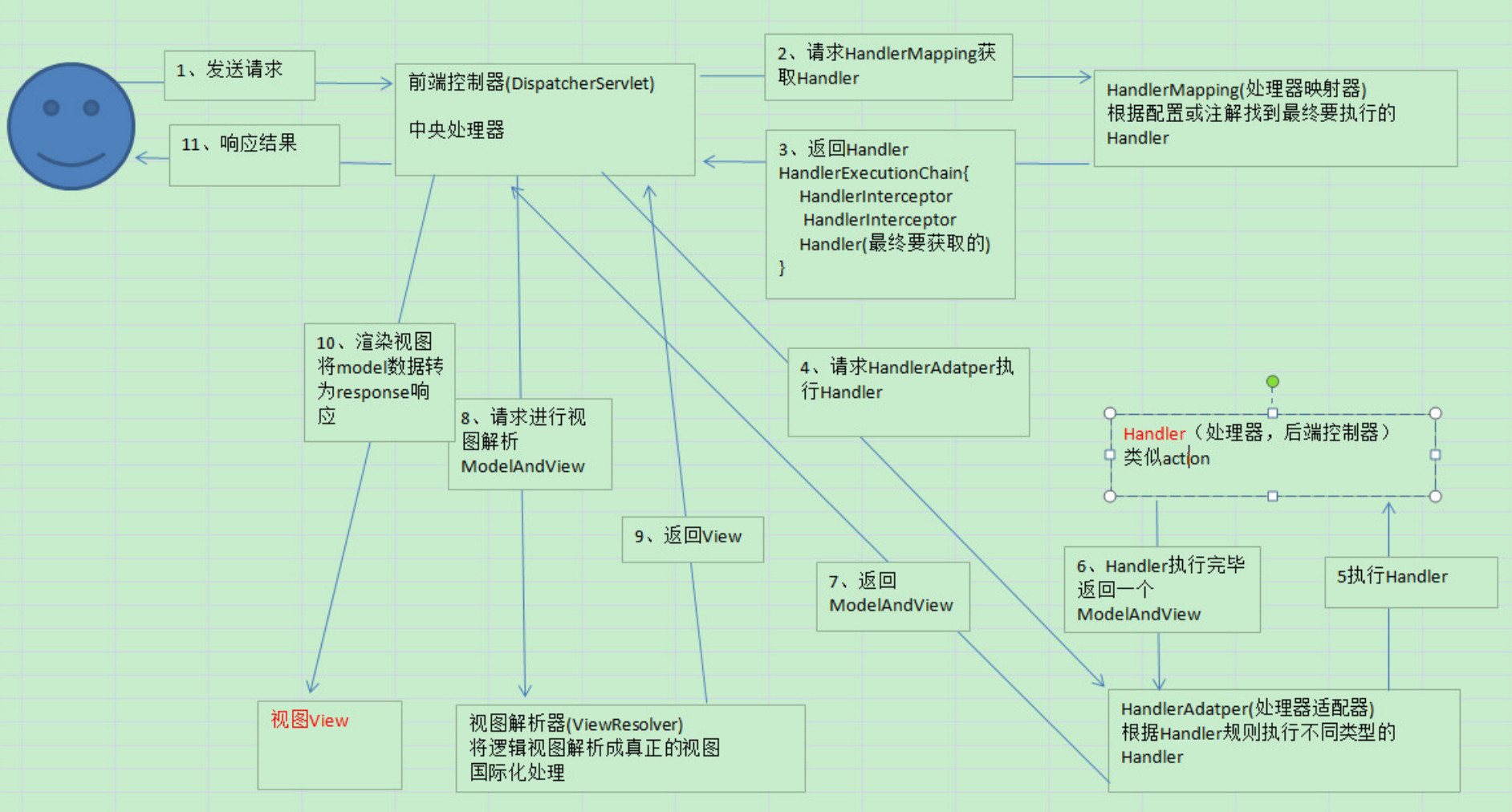
doService()。处理流程
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch}
* for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
//进入doDispatch
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 先处理是否Multipart的请求,如果是则会解析,并且返回一个解析后的请求。
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 寻找对应的handler
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
// 没有找到则直接返回默认404视图。
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 前置拦截器
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 如果上面的流程都执行完成,在执行真实的handle
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 如果是异步的就直接结束。
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 视图解析
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//执行后置拦截器
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 响应视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
// 没有抛异常也会判断是否异步,如果是异步也会执行拦截器。
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
// 遍历所有的HandlerMapping找出对应的HandlerExecutionChain
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
*/
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
// 取出所有拦截器,遍历拦截器
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
}
Spring作用域。
当定义一个Bean时,可以给这个Bean声明一个作用域。通过@Scope注解声明在类上。
- Bean默认作用域是singleton 单例模式,在每个Spring Ioc容器中的一个Bean定义一个实例,也就是无状态Bean,也就是线程不安全的。这个单一实例会被存储到单例缓存(singleton cache)中,并且所有针对该bean的后续请求、访问和引用都将返回被缓存的对象实例。相当于一次创建多次使用。
- prototype 原型模式,在每个Spring Ioc容器中的一个Bean定义多实例,就相当与Java 中new 操作。通常作为有状态的Bean。Prototype作用域的bean会导致在每次对该bean请求(将其注入到另一个bean中,或者以程序的方式调用容器的getBean()方法)时都会创建一个新的bean实例。
spring mvc增加的作用域。
- request、session、global session 仅在基于web的应用中使用(不必关心你所采用的是什么web应用框架)。
- 如果不是在web下实现而是通过ApplicationContext这种实现,尝试使用这些作用域将抛出异常IllegalStateException未知作用域。
- request 对每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean。Spring容器会根据loginAction bean定义创建一个全新的LoginAction bean实例,且该loginAction bean实例仅在当前HTTP request内有效,因此可以根据需要放心的更改所建实例的内部状态,而其他请求中根据loginAction bean定义创建的实例,将不会看到这些特定于某个请求的状态变化。当处理请求结束,request作用域的bean实例将被销毁。
- session 对每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,Spring容器会根据userPreferences bean定义创建一个全新的userPreferences bean实例,且该userPreferences bean仅在当前HTTP Session内有效。与request作用域一样,你可以根据需要放心的更改所创建实例的内部状态,而别的HTTP Session中根据userPreferences创建的实例,将不会看到这些特定于某个HTTP Session的状态变化。当HTTP Session最终被废弃的时候,在该HTTP Session作用域内的bean也会被废弃掉。
- global session 作用域类似于标准的HTTP Session作用域,不过它仅仅在基于portlet的web应用中才有意义。Portlet规范定义了全局Session的概念,它被所有构成某个portlet web应用的各种不同的portlet所共享。在global session作用域中定义的bean被限定于全局portlet Session的生命周期范围内。在一个标准的基于Servlet的web应用,并且定义了一个或多个具有global session作用域的bean,系统会使用标准的HTTP Session作用域,并且不会引起任何错误。
- 作用域依赖
- Spring IoC容器除了管理对象(bean)的实例化,同时还负责协作者(或者叫依赖)的实例化。如果将一个Http request范围的bean注入到另一个bean中,那么需要注入一个AOP代理来替代被注入的作用域bean。也就是说需要注入一个代理对象,该对象具有与被代理对象一样的公共接口,而容器则可以足够智能的从相关作用域中(比如一个HTTP request)获取到真实的目标对象,并把方法调用委派给实际的对象。
- request、session、global session 仅在基于web的应用中使用(不必关心你所采用的是什么web应用框架)。
内嵌web容器
spring boot 可以切换web容器,通过spring boot spi机制,引入不同的web容器并屏蔽默认tomcat完成切换web容器。
- spring-boot-starter-tomcat
- Spring-boot-starter-jettty
- Spring-boot-starter-undertow
- spring-boot-starter-reactor-netty
web配置
web容器配置信息分为两种,配置文件和代码配置。这里主要说下代码配置。
- WebServerFactoryCustomizer
<T>- TomcatServletWebServerFactory
- JettyServletWebServerFactory
- UndertowServletWebServerFactory
扩展
- 重定向,在spring mvc中有一个重定向视图(很少用)
- Redirect: 做了一个http 302的跳转,由客户端发起。(会丢失上一次请求的请求头)
- Forward: 由服务端发起的跳转。